Which of the Following Is the Major Motor Tract
Questions All questions 5 questions 6 questions 7 questions 8 questions 9 questions 10 questions 11 questions 12 questions 13 questions 14 questions 15 questions 16 questions 17 questions 18 questions 19 questions 20 questions 21 questions 22 questions 23 questions 24 questions 25 questions 26 questions 27 questions 28 questions 29 questions 30. Upper motor neuron lesions are characterized by weakness spasticity hyperreflexia primitive reflexes and the Babinski sign.

Accessphysiotherapy Motor Pathways
The first order neurons of these tracts terminate by synapsing in the posterior gray column Rexed laminae I IVV VI with the cells in substantia gelatinosa lamina II.
. These specialized upper motor neurons are called the pyramidal cells of Betz. 3 major types Reflexes Postural adjustments Voluntary movements from simple to complex Diverse adaptive Purposeful Organization of Movements Hierarchical. The white matter forming the ascending and descending spinal tracts is grouped in three paired funiculi or sectors.
Contains major descending voluntary motor tracts for precise movements. The path starts in the motor cortex where the bodies of the first-order neurons lie. In order to achieve spinal anesthesia Novocain is injected into the.
The axons of the corticobulbar tract are ipsilateral meaning they project from the cortex to the motor nucleus on the same side of the nervous system. The cord is shorter than the vertebral canal and thus the. Although normally insignificant which motor tracts can be important in maintaining motor control and muscle.
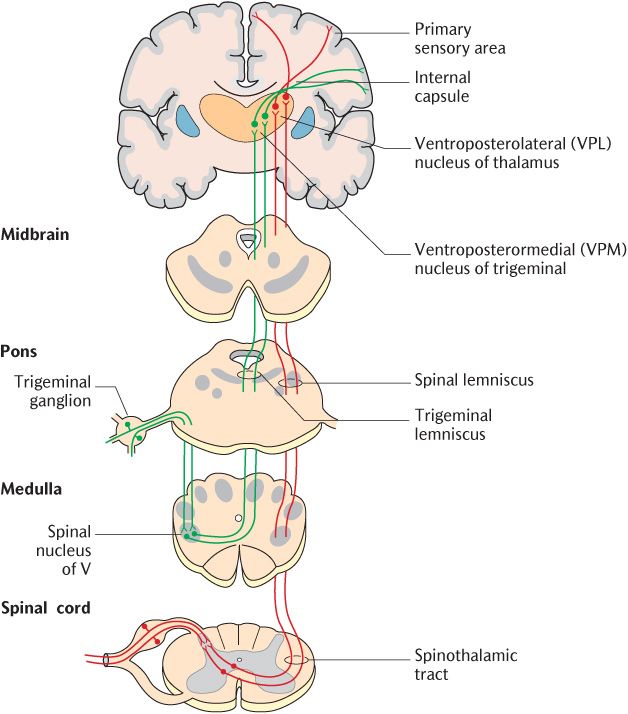
This fifth cranial nerve is a mixed nerve that detects sensations from the scalp face and teeth. Body positioning involuntary movements muscle tone and muscle strength. It includes the following parts.
A hammer strikes the Achilles tendon to elicit this stretch reflex. Ascending tracts are sensory pathways that begin at the spinal cord and stretch all the way up to the cerebral cortex. Delivers sensations to the CNS The cell body is in the dorsal or cranial root ganglion.
These areas are the primary motor cortex Brodmanns area 4 the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor area Figure 31. Any motor command from the primary motor cortex is sent down the axons of the Betz cells to activate upper motor neurons in either the cranial motor nuclei or in the ventral horn of the spinal cord. The dorsal or posterior funiculi lying between the dorsal horns.
3 major types Reflexes Spinal cord circuits. The GI tract extends from Mouth to Anus. Primitive reflexes include the grasp suck and snout reflexes.
An interneuron with the cell body. The dorsolateral tract of Lissauer is a small bundle of both myelinated and unmyelinated fibers. Cauda equina Spinocerebellar Pyramidal Spinothalamic.
Motor circuits-reminiscent of parallel sensory pathways Organization of Movements Hierarchical. The second order neurons cross via the anterior white commissure and ascend. The lateral funiculi lying on each side of the spinal cord.
Also called the spinothalamic tract. The pyramidal tract is a. The Motor System Examination.
They are made up of four successively connected neurons. Axons in the ___________ descending tracts synapse on lower-motor neurons in the motor nuclei of several cranial nerves and control skeletal muscles that move the eye jaw face and some of the neck and pharynx muscles. It is cylindrical in shape and has cervical and lumbar enlargements where the nerves supplying the upper limb C5T1 and lower limb L1S3 originate.
The spinal cordthe ventral horns composed of motor neurons. The anatomy of the important sensory and motor tracts within the white matter of the spinal cord. The motor system evaluation is divided into the following.
Sensory and Motor Tracts The three major sensory tracts involve chains of neurons. Which of the following is the major motor tract. There are three types of ascending tracts dorsal column-medial lemniscus system spinothalamic or anterolateral system and spinocerebellar system.
The major motor tract that originates in the precentral gyrus. Axons from the corticospinal tract CSTor pyramidal tract carry information from the precentral gyrus brodmann area 4 of the motor cortex the supplemental and premotor cortices area 6 to Lower motor neurons LMNs which will synapse with muscle cells in the body effecting voluntary movement. Monitors ongoing movement and equilibrium.
Lets have a little discussion of each of it. Other articles where motor tract is discussed. It is responsible for the voluntary movements of the limbs and trunk.
While most of the fibers from this tract are from the motor cortex. The corticospinal tract is a motor pathway that carries efferent information from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. The motor cortex comprises three different areas of the frontal lobe immediately anterior to the central sulcus.
Electrical stimulation of these areas elicits movements of particular body parts. Coming to the structure of the GI tract It is a hollow muscular tube that is approximately 30 inches or 9 meters long. The adult spinal cord is about 45 cm long.

16 Major Sensory And Motor Systems Pocket Dentistry


0 Response to "Which of the Following Is the Major Motor Tract"
Post a Comment